 Warts, also known as verrucae, are common viral infections caused by the Human papilloma virus, leading to an increase in epithelial and keratin production. The onset of these lesions can vary from a few weeks to more than a year. Their clinical appearance depends on the subtype of the wart, the area of the body it affects, and the individual's immune status. Warts are highly contagious, and if treatment is delayed, they can spread rapidly, making treatment progressively challenging. Hence, it's crucial to start treatment early.
Warts, also known as verrucae, are common viral infections caused by the Human papilloma virus, leading to an increase in epithelial and keratin production. The onset of these lesions can vary from a few weeks to more than a year. Their clinical appearance depends on the subtype of the wart, the area of the body it affects, and the individual's immune status. Warts are highly contagious, and if treatment is delayed, they can spread rapidly, making treatment progressively challenging. Hence, it's crucial to start treatment early.
Most individuals with warts are generally healthy in other aspects. However, those with diseases causing immunosuppression or those using immunosuppressive drugs like corticosteroids, and organ transplant recipients may have an increased likelihood and severity of warts. Warts are benign skin growths, commonly found on hands, feet, face, or the genital area. They can spread through direct contact or by touching infected items. Genital warts are frequently transmitted through sexual contact. The diagnosis of warts is primarily based on clinical appearance.
In treating warts, factors such as the patient's age, the extent and duration of the lesions, the patient's immune status, and the patient's treatment preference should be considered. Some patients may require short-term treatment, while others may need recurring, prolonged treatments.
Cryotherapy (Liquid Nitrogen): Cryotherapy is the most commonly used treatment method for warts. Lesions are frozen using liquid nitrogen at -196°C. The main disadvantage of this freezing process is that it can be painful. Cryotherapy should be applied every 15 days until all lesions have disappeared.
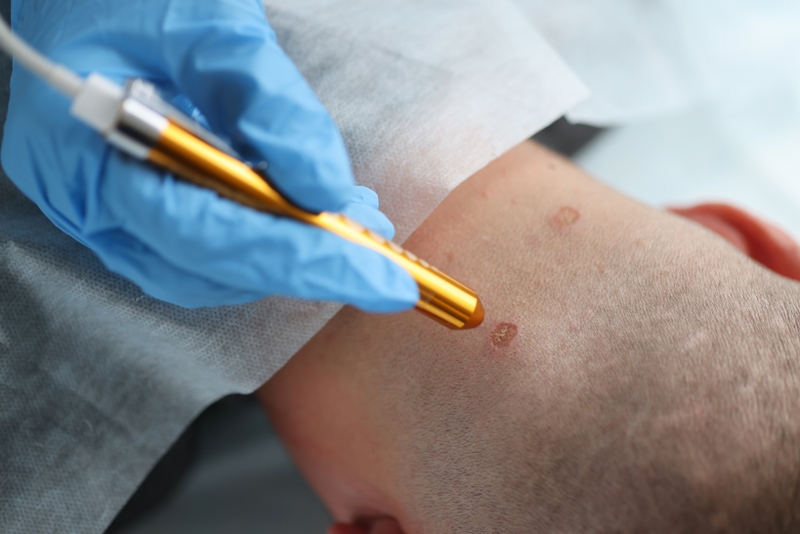
Electrocauterization: This method is often preferred when the number of lesions is small. Local anesthesia is required using needles. One of the advantages of this method is that the treatment can be completed in a single session.
Chemical Agents: Chemicals such as salicylic acid in concentrations ranging from 10% to 40% can be used in the form of creams, gels, and certain ointments. Additionally, antimitotic agents like podofilin can also be utilized.